Chapter 6. Network Configuration
Red Hat Linux no longer includes the application netcfg to configure your network devices. The Red Hat Network Administration Tool has replaced netcfg and can be used to configure the different types of network devices: Ethernet, Modem, ISDN, xDSL, CIPE, and Wireless.
You can also configure a modem, ISDN, or an xDSL connection with internet-druid. Refer to the Official Red Hat Linux Getting Started Guide for more details on internet-druid.
To use the Red Hat Network Administration Tool, you must be running the X Window System and have root privileges. To start the application, use one of the following methods:
On the GNOME desktop, go to the Main Menu Button (on the Panel) => Programs => System => Network Configuration.
On the KDE desktop, go to the Main Menu Button (on the Panel) => Red Hat => System => Network Configuration.
Type the command neat at a shell prompt (for example, in an XTerm or a GNOME terminal).
If you make any changes to your network configuration using this tool, you must click the Apply button to have the changes take effect.
If you prefer modifying the configuration files, refer to the Official Red Hat Linux Reference Guide for information on their location and contents.
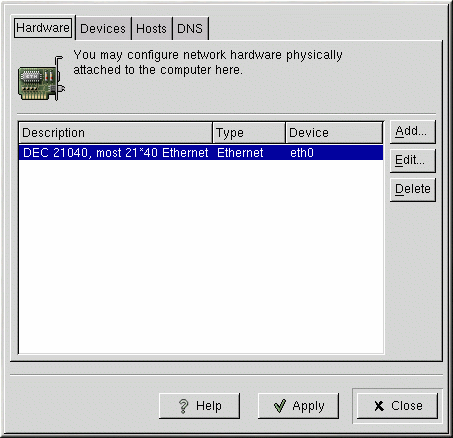
Adding Network Hardware
From the main Red Hat Network Administration Tool window, use the Hardware tab to add, edit, or delete Ethernet, modem, ISDN, and token ring hardware configurations.
Ethernet
You can configure the type of adapter (manufacturer and model) and kernel device name for an Ethernet device. The type of adapter you select determines which kernel module (driver) is loaded for the network interface card. After selecting the adapter, select the kernel device name for the network interface card (/dev/eth0, /dev/eth1, and so on). You can also configure the device's system resource settings such as IRQ. After configuring the hardware settings for the Ethernet device, go to the Device tab to configure its network settings such as using DHCP to obtain an IP address.
Modem
For a modem, you can configure the kernel device name, baud rate, flow control, modem volume, and whether to use touch tone dialing. If you want to configure a modem Internet connection, go to the Device tab and select Modem as the Device Type.
ISDN
For an ISDN device, you can configure the adapter (manufacturer and model), system resources (such as IRQ), and D Channel Protocol. If you want to configure an ISDN Internet connection, go to the Device tab and select ISDN as the Device Type.
Token Ring
For a token ring device, you can select the type of adapter according to the manufacturer and model of the device. The type of adapter determines which kernel modules (driver) is loaded for the device. You can also configure the kernel device name (/dev/tr0, /dev/tr1, and so on) and the device's system resources such as IRQ. After configuring the hardware settings for the token ring device, go to the Device tab to configure its network settings such as using DHCP to obtain an IP address.